Our Blogs
Stay Updated with Student Visa News & Study Abroad Tips
Discover expert advice, visa updates, and helpful resources to guide your journey to studying abroad.
Top Scholarships for International Students in 2025
For many ambitious students, studying abroad is a life-changing dream that...
Top 5 Countries for International Students in 2025
Studying abroad has become one of the most rewarding investments for...

Join a Global Education Network
Expand your horizons by connecting with a global education network. Access top institutions, expert guidance, invaluable resources, and life-changing experiences to pursue your study abroad dreams, gain cultural exposure, and achieve academic success worldwide
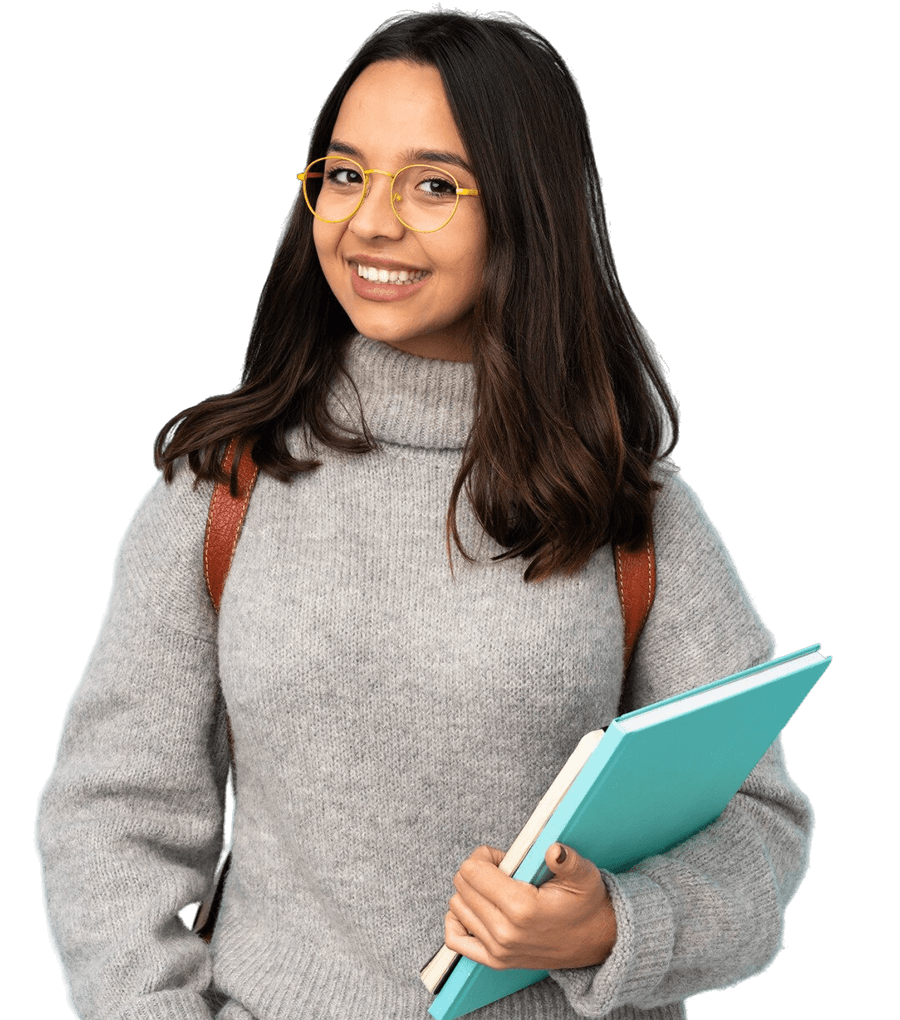

What are Families & Companies Saying About Us
We’ve worked with many tech providers in the past, but nothing compares to the performance and reliability of this solution. It’s intuitive, powerful, and exceeded our expectations from day one.
– Amit R., CTO at NexaCloud
New York
We’ve worked with many tech providers in the past, but nothing compares to the performance and reliability of this solution. It’s intuitive, powerful, and exceeded our expectations from day one.
– Amit R., CTO at NexaCloud
New York
We’ve worked with many tech providers in the past, but nothing compares to the performance and reliability of this solution. It’s intuitive, powerful, and exceeded our expectations from day one.
– Amit R., CTO at NexaCloud
New York
What are Families & Companies Saying About Us
Frequently asked Questions
How do I know which visa type is right for me?
Solar panels on your roof capture sunlight, turning it into direct current (DC) electricity. A solar inverter then transforms this into alternating current (AC), which powers your home’s appliances.
Any extra solar power your home doesn’t use can go two ways: it can be sent back to the electricity grid, potentially earning you credits. Or, if you have a solar battery, that excess energy can be stored for later use. This means you can power your home at night, during expensive peak hours, or even have short-term backup during a blackout.
How long does the visa application process usually take?
Solar panels on your roof capture sunlight, turning it into direct current (DC) electricity. A solar inverter then transforms this into alternating current (AC), which powers your home’s appliances.
Any extra solar power your home doesn’t use can go two ways: it can be sent back to the electricity grid, potentially earning you credits. Or, if you have a solar battery, that excess energy can be stored for later use. This means you can power your home at night, during expensive peak hours, or even have short-term backup during a blackout.
What documents are required for a visa application?
Solar panels on your roof capture sunlight, turning it into direct current (DC) electricity. A solar inverter then transforms this into alternating current (AC), which powers your home’s appliances.
Any extra solar power your home doesn’t use can go two ways: it can be sent back to the electricity grid, potentially earning you credits. Or, if you have a solar battery, that excess energy can be stored for later use. This means you can power your home at night, during expensive peak hours, or even have short-term backup during a blackout.
Do you guarantee that my visa will be approved?
Solar panels on your roof capture sunlight, turning it into direct current (DC) electricity. A solar inverter then transforms this into alternating current (AC), which powers your home’s appliances.
Any extra solar power your home doesn’t use can go two ways: it can be sent back to the electricity grid, potentially earning you credits. Or, if you have a solar battery, that excess energy can be stored for later use. This means you can power your home at night, during expensive peak hours, or even have short-term backup during a blackout.
Do you provide support for multiple countries?
Solar panels on your roof capture sunlight, turning it into direct current (DC) electricity. A solar inverter then transforms this into alternating current (AC), which powers your home’s appliances.
Any extra solar power your home doesn’t use can go two ways: it can be sent back to the electricity grid, potentially earning you credits. Or, if you have a solar battery, that excess energy can be stored for later use. This means you can power your home at night, during expensive peak hours, or even have short-term backup during a blackout.
What happens after my visa is approved? Ask ChatGPT
Solar panels on your roof capture sunlight, turning it into direct current (DC) electricity. A solar inverter then transforms this into alternating current (AC), which powers your home’s appliances.
Any extra solar power your home doesn’t use can go two ways: it can be sent back to the electricity grid, potentially earning you credits. Or, if you have a solar battery, that excess energy can be stored for later use. This means you can power your home at night, during expensive peak hours, or even have short-term backup during a blackout.
Have Questions? Get in Touch!
Phone Number
02-41070218
Email Address
info@immigrationexpressbd.com
Office Address
Monir Tower , Suite # 12/D, 167/1 DIT Extension Road , Fakirapool, Motijheel C/A, Dhaka – 1000, Bangladesh